Multiple Choice
Questions (12 points, 2 each): answer the following multiple choice
questions by circling the best response in each case.
1. The Cl-C-Cl bond angle in the COCl2 molecule is approximately:
- 92o
- 104.5o
- 114o
- 123o
- greater than 180o
2. The hybridization of the central atom in ICl2 - anion is
- sp
- sp2
- sp3
- sp3d
- sp3d2
3. Which of the following reactions will have the largest DE value?
a. Cu(g) g Cu+(g) + e-
b. Mg(g) g Mg+(g) + e-
c. S(g) g S+(g) + e-
d. Si(g) g Si+(g) + e-
e. Cs(g) g Cs+(g) + e-
4. Which of the following molecules cannot form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule?
a. NH3
b. H2O
c. HF
d. CH4
e. CH3OH
5. How many electrons can have the following quantum numbers: n = 4; l = 2; ms = -½
a. 2
b. 3
c. 5
d. 6
e. 10
6. The heat energy that one gram of a substance needs to absorb in order for its temperature to increase by 1oC (1 K) is called its
a. kinetic energy
b. specific heat capacity
c. heat transfer
d. calorimetry
e. enthalpy of formation
Short
Answer (40 points, 4 each): answer each of the following short-answer
questions
7. Calculate the temperature change that occurs when 30.0 kJ of heat is
added to 1.00 kg of H2O (s(H2O) = 4.184 kJ/kg °C)
8. Identify (name and structure) the product(s) of the reaction between 1 mole of 2-butyne and 1 mole of chlorine (Cl2).
9. Write electron configurations for the following atoms and ions:
Br:
N-:
Fe3+:
Cu:
10a. Under what set of conditions will a reaction never be spontaneous?
b. Is it correct to say that a non-spontaneous reaction can never be made to occur? Justify your answer (briefly).
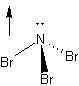
11. Does the NBr3 molecule have a dipole
moment? If so, in which direction does the dipole point? (indicate with a
suitable structure/picture)
12a. Indicate the major (strongest) intermolecular force that exists in samples of each of the following compounds.
b. Circle the one that should possess the highest boiling point.
C5H11OH ________________________
NO ________________________
C6H14 ________________________
13. Iodide ion is oxidized in acidic solution to triiodide ion, I3-, by hydrogen peroxide.
H2O2 (aq) + 3I- (aq) + 2H+ (aq) à I3- (aq) +2H2O (l)
A series of four experiments was run at different concentrations and the initial rates of formation for I3- were determined.
Exp. number
[H2O2], M [I-],
M [H+], M Initial rate, M/s
1 0.010 0.010 0.00050 1.15
x 10-6
2 0.020 0.010 0.00050 2.30 x 10-6
3 0.010 0.020 0.00050 2.30 x 10-6
4 0.010 0.010 0.00100 1.15 x 10-6
From these data,
(a) Obtain the reaction orders with respect to H2O2, I-, and H+.
(b) Write
the rate law
14. The reaction to form aA à Products is second order with a rate constant of 0.413 M-1. s-1. What is the half-life, in seconds, of the rxn if the initial concentration of A is 5.25 x 10-3 M?
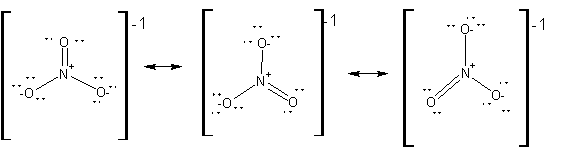
15. Consider the nitrate anion, NO3-
a. Write all appropriate Lewis structures.
b. Indicate the formal charges on the nitrogen and oxygen atoms for one of these structures.
16. For the following reaction, calculate the C-H bond energy given the following data.
CO(g) +2H2(g) à CH3OH(l) ΔHrxn = -128 kJ
Bond D (kJ/mol)
C≡O 1072
H-H 436
C-O 358
O-H 467
Long
Answer (48 points, 8 each): answer each of the following questions in the
space provided
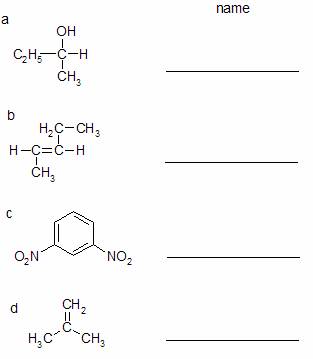
17. Next to each structure below, indicate each structure’s complete systematic name.
18. Write an equation expressing the enthalpy of formation for CuO(s). Given the following thermochemical equations:
2Cu(s) + S(s) à Cu2S(s) DHo = -79.5 kJ
S(s) + O2(g) à SO2(g) DHo = -297 kJ
Cu2S(s) + 2O2(g) à 2CuO(s) + SO2(g) DHo = -527.5 kJ
Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation (in kilojoules per mole) of CuO(s).
19. The reaction 2 NO2(g) D N2O4(g) has DG° = -5.40 kJ/mol of N2O4, at 25°C. In a reaction mixture, the partial pressure of NO2 is 0.25 atm and the partial pressure of N2O4 is 0.60 atm. In which direction must this reaction proceed to reach equilibrium? Explain, using appropriate calculations.
20. When heated, ethyl chloride, CH3CH2Cl, decomposes in a first order reaction to give ethylene and hydrogen chloride.
CH3CH2Cl (g) à C2H4 (g) + HCl (g)
In an experiment, the initial concentration of ethyl chloride was 0.001M. After heating at 500 0C for 155 s, this was reduced to 0.00067M. What is the concentration of ethyl chloride after a total of 256 s?
21.
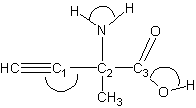
For the structure above, report
a. the total number of lone pairs of electrons __________________
b. the total number of π-bonds __________________
c. the values of the CC1C2, HNH, and HOC3 bond angles (denoted with the “arch” sign)
Bond angles
CC1C2 ___________________
HNH ___________________
HOC3 ___________________
d. hybridization of the C1 , C2, and C3 atoms
Hybridization
C1 ___________________
C2 ___________________
C3 ___________________
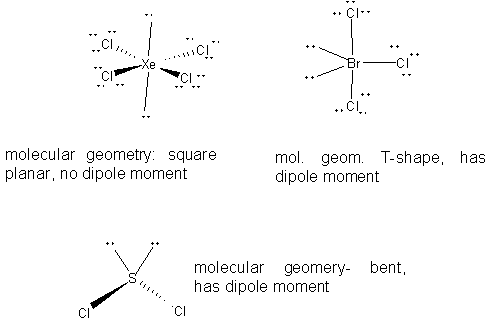
22a. Using the VSEPR theory, draw the structures of
XeCl4
BrCl3
SCl2
b. Circle the structure(s) with non-zero dipole moments, if any.
![]() Equations
Equations
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
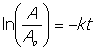
![]()
![]()
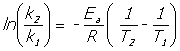
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
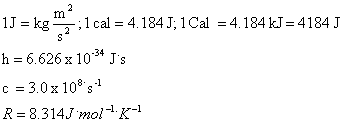
![]()
![]()
q = m s Δt
Answers:
Multiple
choice:
1. (c); 2. (d) 3. (c) 4. (d) 5. (c) 6. (b)
Short
Answers
7. q = m s Δt; 30.0 kJ = 1.00 kg x 4.184 kJ/kg 0C Δt; Δt = 30.0/(4.184 x1.0) = 7.2 °C
temperature will increase by 7.2 °C.
8. trans-dichloro-2-butene (major product) and cis-dichloro-2-butene (minor product)
9. Br: [Ar]3d104s24p5; N-: 1s22s22p4; Fe+3: [Ar]3d5; Cu: [Ar]3d104s1
10. a)ΔS<0; ΔH>0, gives ΔG>0 b) no, it can be made to occur (ΔG= ΔH-T ΔS) by varying temperature and, thus, the entropy factor.
11. The molecule has a trigonal pyramidal structure, with electron density shifted from Br atoms towards more electronegative N-atom.
12. H-bonding, dipole-dipole, dispersion. C5H11OH has the highest boiling temperature.
13. (a) [H+]0; [I-]1 [H2O2]1 (b) rate= k [H2O2][I-]
14. t1/2 = 1/(k x [A0]) = 1/(0.413 M-1s-1 x 5.25 x 10-3 M) = 461 s
15.
16. ΔH = Σ D(bond broken) – ΣD (bond formed)
ΔH = (C≡O) + 2(H-H) –[ 3(C-H) + C-O + O-H] = 1072 + 2x436 – 3(C-H) – 358-467 = -128
x= 416 kJ/mol = C-H bond dissociation energy
Long Answers
17 a) 2-butanol; b) trans-2-pentene; c) meta-dinitrobenzene d) methylpropen
18. 2Cu(s) + S (s) à Cu2S (s) -79.5 kJ
SO2 (g) à S(s) +O2 (g) + 297 kJ
Cu2S (s) + 2O2 (g) à 2CuO(s) + SO2 (g) -527.5 kJ
2Cu(s) + O2 (g) à 2CuO(s) -310 kJ
for one mole of Cu (s) : -310/2 = -155kJ/mol
19. ΔG = 0 at equilibrium; ΔG = ΔG0 + RT lnQ=0; ΔG0 = -RTlnK
5400J/mol = 8.314 J/mol K 298.2K lnK; lnK = 2.178; K =8.8
Q = (0.60/0.252) = 9.6; Q>Keq, therefore, rxn must proceed in reverse direction to reach equilibrium.
20. ln[A]t = ln[A]0 –kt
find k: ln(0.000670) = ln(0.001) –kx 155 ; k= 2.584 x 10-3 s-1
find concentration after 256s using k
ln[A]t = ln (0.0010) – 2.584 x10-3 s-1 x 256s
[A]t = e-7.5692 = 5.16 x 10-4M
21.a) 5, b) 3 c) CC1C2 = 1800; HNH <109.5; HOC3 <109.5
d) C1 sp; C2 sp3, C3 sp2
22.