QUIZ#3 CHEM100.11 February 15, 2012
Name: ___________________
Family name First name
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN:
This test comprises 10 pages (including this page) and a Periodic Table. Please make sure you have a complete exam and
that you have filled in the information above.
All questions are to be answered on the question sheets. Calculators are permitted. You have 50 min.
Useful equations, constants and conversion factors:
R = 8.314 J/mol K
J = kg m2 s-2
1 cal = 4.18 J
![]()
![]()
Arrhenius equation: Integrated forms:
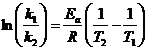
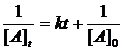 differential rate law: rate = k [A]n [B]m
[C]p…..
differential rate law: rate = k [A]n [B]m
[C]p…..
Integrated Rate Laws: ln[A]t = -kt + ln[A]0
![]()
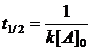
qsolution = -q reaction = m × specific heat × DT
DG° = DH° - TDS°
DG = DG° + RTlnQ DG° = - RT lnKeq
DHrxn = ΣnDHf0products - ΣnDHf0reactants
SHORT ANSWERS {4problems x10 scores, 40 scores, }
- {10} A first-order reaction has a rate
constant of 2.75x10-2 s-1 at 20.0 oC.
(6)
What is the
value of k at 60.0 oC if Ea = 75.5 kJ/mol?
{4} Calculate half-life for
each temperature.
2. {10} A pound (454g) of plain M&M candies contains 96 g of fat,
320 g of carbohydrate, and 21 g of protein.
What is the energy value, in dietary (nutrition) Calories, of this
amount of candies?
Fuel values:
carbohydrate and protein : 17 kJ/g
fat 38 kJ/g
3. {10} Consider the reaction
3CH4(g) D C3H8 (g) + 2H2
(g)
For this rxn, ΔGo = 128.9 kJ/mol
Calculate ΔG at 298 K for the rxn
mixture that consists of 40.0 atm CH4
, 0.01 atm C3H8 and 0.018 atm H2
- {10} SO2Cl2
decomposes in the gas phase by the reaction
SO2Cl2 (g) à
SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
The reaction is first order in SO2Cl2 and the
rate constant is 3.0 x 10-6 s-1 at 600 K. A vessel is
charged with 2.4 atm of SO2Cl2
at 600K. Calculate the partial pressure of SO2Cl2 after
3.0 x 105 s.
Longer Problems {3 problems x 20 scores}
- {20} When a
4.25-g sample of solid ammonium nitrate dissolves in 60.0 g of water in a
coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature drops from 22.0 oC to 16.9 0C. Calculate ΔH (in kJ/mol NH4NO3)
for the solution process:
Assume that specific heat of the solution in calorimeter is the same as
for water, 4.184 J/g oC.
6. {20}
a. {15} Using the date from
the Table below, calculate the equilibrium constant at 100 oC
for the following rxn:
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) D
2 SO3 (g)
b. {4} At
which temperature reaction will be at equilibrium?
c. {1} Would
you increase or decrease temperature in order to make the reverse rxn spontaneous?
Table
substance ΔHof (kJ/mol) S (J/mol K)
SO2 (g) -297 249
O2 (g) 0 205
SO3 (g) -395 256
7. {20} the data below were obtained for the rxn:
aA + bB + cC à
dD + eE
Exp. [A], M [B], M [C] Initial rate, M/s
1 0.020 0.010 0.01 1.15 x 10-2
2 0.040 0.010 0.01 1.15 x 10-2
3 0.030 0.020 0.01 2.30
x 10-2
4 0.020 0.020 0.005 5.75
x 10-3
(a) {15} write down the rate law for this rxn
(b) {1} what is the overall order for this rxn?
(c) {3} calculate the rate constant for this rxn (show units!)
(d) (1) what is the
initial rate at [A] =[B] = [C] =0.1?
Answers:
- ln(k1/k2) = 75500/8.314 (1/293-1/333)= 3.723; k1/k2=
41.4; k1(60)=0.0275x41.4= 1.13 s-1
t 1/2 (20oC) = 0.693/0.0275 s-1 = 25.2 s; t 1/2 (60 oC) = 0.693/1.13 s-1 = 0.613 s
- 96g x
38 kJ/mol + (320 g + 21 g) 17 kJ/g = 9445 kJ
2249
kcal or 2249 Cal
- DG = DG° + RTlnQ ;
Q = P(propane)P2(H2)/P3
(CH4)
Q= 0.01 x 0.0182/403=
5.06 x 10-11
lnQ=
-23.7
ΔG = 128.9 kJ/mol - 0.008314 kJ/mol K x 298K x 23.7 = 70.2 kJ mol
4. lnP = -kt + ln[P] = -3.0 x 10-6 x 3.0 x 105 + ln[2.4] = -0.0245
[P]= e-0.0245 = 0.98 atm
5. M NH4NO3= 28+4+48= 80
g/mol
4.25g/80 g/mol = 0.053 mol
qrxn = -qsol
ΔH =qrxn = -4.184 J/g oC
x 64.25g (16.9 -22.0oC) = 1371 J (endothermic)
ΔH= 1.371kJ/0.0531mol = 25.8 kJ/mol
- (a) ΔHorxn
(kJ/mol)
= 2(-395) –2(-297) = -196 kJ/mol
ΔSorxn
(J/mol) = -191 J/mol
K = -0.191 kJ/mol K
ΔGrxn
(kJ/mol) = -196 kJ/mol -373K(-0.191 kJ/mol K) = -124.8 kJ/mol
lnKeq = - ΔGrxn
/RT = 124.8 kJ/mol / 0.008314 kJ/mol
K x 373 K = 40.2
Keq
= e40.2 =
2.87 x 1017 at 100 oC
(b)
T= 196/0.191 = 1026 K
(c) Increase
- (a) exp 2 and 1: [C] = [B]
= constant, 2 fold increase in [A] no
change in the rate
zero order in A
exp. 2 and 3: [C]
is constant; 2-fold
increase in [B] caused 2-fold increase
in the rate: [2]m = 2; m=1; rxn is 1st
order in [B]
exp. 4 and 3 {B]=constant, 2 fold increase in [C] causes 4-fold increase in
rate:
rxn is second order in C rate = k [C]2[B]
(b) overall rxn order: 2+1 = 3
(c) rate constant, k
0.0115 M/s = k (10-2
M)2 (10-2 M)= k 10-6
M3
k = 0.0115 Ms-1/
10-6 M3 = 0.0115 x 106 = 1.15 x104 s-1M-2
d) rate= 1.15 x104 s-1M-2 (0.1M)3 = 1.15 x104 x 10-3 = 11.5 M s-1