 |
Mass Spectroscopy, Example #1
Analysis: C5H12O MW = 88.15
Help with Analysis
Mass Spectrum
| Correlation Table | Common Fragments | Interpret MS |
| Give Structure | Next Example | Return to MS Home |
 |
Mass Spectroscopy, Example #1
Analysis: C5H12O MW = 88.15
Help with Analysis
| Correlation Table | Common Fragments | Interpret MS |
| Give Structure | Next Example | Return to MS Home |

From the molecular formula, the compound has "no degrees of unsaturation" (no double bonds, carbonyls or rings).

Fragmentation of Common Functional Groups
The spectrum shows a small molecular ion and a small m-1 peak, suggesting the presence of an alcohol (it cannot be an aldehyde since there are no degrees of unsaturation). The m-15 peak represents loss of a methyl group and the m-17 is consistent with loss of a hydroxy radical. For an alcohol, the base peak is often formed by expulsion of an alkyl chain to give the simple oxonium ion R'CR''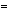 OH+; to generate the observed m/e = 45, R' must be CH3 and R' a H.
OH+; to generate the observed m/e = 45, R' must be CH3 and R' a H.
Common Ions and Fragments
