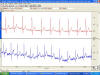
 |
Electrocardiograms from two subjects. Which tracing
would you consider to be from the larger subject? What two lines of
evidence can you use to make your decision?
|
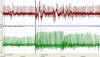 |
These tracings show
the EKG (top) and Peripheral Pulse (bottom) prior to exercise (to the
left of the dark vertical line) and after exercise (to the right of the
dark vertical line). The amount of time between vertical pale grey
vertical grid lines is 6.75 s; do not confuse the two medium-gray
markers (Control-Exercise, post-exercise) as grid lines.
By what percentage did the heart
rate increase from the control period to immediately after exercise? Did
the heart rate get back to normal by the end of the experiment? What
accounts for the waviness in the EKG baseline after exercise? What about
the one bout of waviness about 1/3 of the way into the control period?
Comment on the peripheral pulse. |
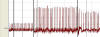 |
Leads I, II and III - electrocardiograms taken in lab.
Explain why these leads give rise to different EKGs. |
 |
A 12-lead electrocardiogram; why do the 12 leads look different from one
another? When do paramedics/hospital staff use this instead of the 3-lead EKG?
What is the progression of ailments that can be diagnosed using the 12-lead EKG,
as described by Ivan Cozzi (the Paramedic)?
|
 |
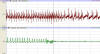
Great EKGs are being recorded until about halfway through this
tracing. Explain the disturbance.
|
 |
Upper tracing, the electrocardiogram. Lower tracing, peripheral pulse.
At the marker, the subject immersed his face into a bowl of water.
Describe the results (i.e. what happened)? Which cranial nerve detects
sensory input in the face? Both the parasympathetic and sympathetic
nervous systems are involved here - what are their roles? |
| |
|
| |
|

